Using AI tools
This guide helps you make informed decisions about when and how to use AI responsibly at Otago Polytechnic.
Understanding GenAI at OP

What is Generative AI (GenAI)?
Generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) is a tool that creates written, visual, or audio content based on prompts you give it. Popular GenAI tools include ChatGPT, Google Gemini, Midjourney and Microsoft Copilot.
How do they work?
GenAI tools are Large Language Models (LLMs). They analyse massive amounts of text and images to learn patterns. When you give them a prompt, they generate responses by predicting what words or images are most likely to come next, based on similar examples in their training data.
Important: GenAI is not a search engine. It creates content by predicting what should come next, which means it can produce confident-sounding answers that are completely wrong (called “hallucinations”).
The three essentials of AI use at OP
Otago Polytechnic’s AI Policy sets out clear expectations for all tauira:
The three essentials
Never input personal, institutional, or sensitive information into public AI tools. This includes:
• Your personal details or those of others
• Work that isn’t your own
• Confidential workplace or organisational information.
Microsoft Copilot is our only OP-approved and supported AI tool for working with organisational data because it upholds privacy and security standards we need. External tools can be useful for personal exploration, but don’t use your OP email or share sensitive information with them.
AI can't do the learning for you. Your work must demonstrate your own understanding, critical thinking, and original contribution.
Always:
• Follow the specific guidelines for AI use – both from OP and from your teacher
• Be transparent about your AI use and declare how you use it
• Remember that being open is more important than being right!
Just because something is permitted, doesn’t make it right. Consider the ethical use of AI and check for:
• Bias
• Tone
• Policy fit
• Accuracy
AI should help you learn not replace your learning.
Our ethical framework
At OP, we’re guided by an ethical framework that ensures AI use aligns with our values and Te Tiriti o Waitangi obligations. The framework covers seven key areas.
-
3. Transparency and explainability
We explain clearly when and how AI is being used and encourage critical dialogue about its use.
-
4. Data privacy, security, and Māori data sovereignty
We protect learner and staff data and uphold Māori data sovereignty as a right under Te Tiriti o Waitangi.
-
5. Regulatory compliance and risk-based governance
AI tools are classified by risk level with appropriate safeguards and regular reviews.
-
6. Kaiako and ākonga empowerment and AI literacy
We support everyone to develop confident, critical AI literacy and reflective practice.
-
7. Responsible AI deployment and continuous evaluation
AI implementation is iterative and adaptive, with diverse stakeholder involvement including Māori and Pacific Peoples.
-
1. Human-centred and ethical AI use
AI supports teaching and learning relationships - it doesn’t replace them. Humans remain at the centre of all significant decisions.
-
2. Equity, inclusion, and fairness
We design AI use to be accessible for all learners and actively work to identify and address bias in AI systems.
Using AI appropriately
Not sure if AI use is appropriate for your task? Here’s a framework to help you think it through:
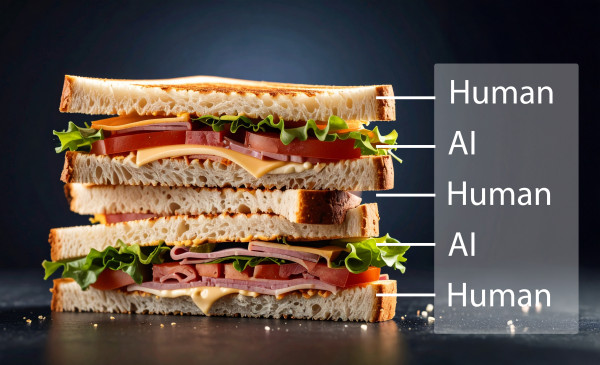
Keep humans at the centre
Think of AI interaction like a sandwich: you are the bread, AI is the filling. You make the decisions at the start (what to ask, what context to provide) and at the end (evaluating, refining, and taking responsibility for the output). AI provides support in the middle.
This means that you decide what questions to ask and how to frame them:
You:
- Critically evaluate everything AI produces
- Take full responsibility for any content you use
- Bring your own knowledge, creativity, and judgement to the task
Questions to ask yourself
Before using AI for any assessment task, consider:
Have you checked with your kaiako about AI use for this assessment?
Does the assessment guidance specifically permit or prohibit AI tools?
Will using AI support your understanding, or replace it?
Can you explain the thinking behind the work you submit?
Are you building skills you’ll need in your future career?
Can you clearly describe how you’ve used AI?
Are you prepared to declare your AI use?
Would you be comfortable explaining your process to your kaiako?
Are you putting any personal or sensitive information into the tool?
Is the tool appropriate for the type of data you’re working with?
Are you using OP-approved tools when working with organisational information?
Does the final work reflect your own voice and understanding?
Have you added your own analysis, perspective, and critical thinking?
Can you defend and discuss the ideas without AI assistance?
AI supporting your learning
AI can be a valuable learning tool when used appropriately. The difference between appropriate and inappropriate use comes down to three things:
-
Learning: Are you using AI to support your understanding, or to bypass learning?
-
Ownership: Is the final work demonstrably yours - your thinking, your voice, your analysis?
-
Transparency: Are you honest about your process and prepared to explain it?
Ākonga examples
Here are examples organised by common learning tasks, with prompts to help you think through appropriate use.
-
Appropriate use
Learning: Using AI to build understanding
Chao-Xing needs to decide on a research topic relating to small businesses in Aotearoa. She can’t think of one that really interests her, so she uses a GenAI tool to generate ten potential topics. She reviews these, chooses one that aligns with her interests and course requirements, then conducts her own research to develop it further.
Why this works:
Chao-Xing uses AI to overcome initial uncertainty, but she makes the final decision and does her own research. The AI helps her thinking process without replacing it.
Inappropriate use
Max is asked to develop three concepts for fusion cuisine. He asks a GenAI tool to brainstorm twenty possibilities, then selects the best three and presents them as his own ideas without any further development or critical engagement.
Why this doesn’t work
Max hasn’t demonstrated his own creative thinking or understanding. He’s submitted AI-generated ideas as his own work.
-
Appropriate use
Articulation: Using AI to express your ideas
Sione is asked to use GenAI to create an initial design that he will then develop and stylise himself. He generates a base design using DALL-E, then significantly modifies, develops, and personalises it using his own skills and creative vision. He provides an in-text citation: (OpenAI, 2023) and full reference: OpenAI (2023). DALL-E (March 14 version) [Deep learning model]. https://labs.openai.com/
Why this works
Sione uses AI as a starting point, but the final work demonstrates his own creative development and technical skills. He’s transparent about his process and properly cites the AI tool.
Inappropriate use
Zoe has to write an essay exploring practices within care of Māori patients that uphold Te Tiriti o Waitangi. She types the question into a GenAI tool, copies and pastes the answers into her essay, changes a few words and phrases, and submits it as work she has done herself.
Why this doesn’t work
Zoe hasn’t demonstrated understanding of Te Tiriti or culturally responsive care. The essay doesn’t reflect her own learning, voice, or critical analysis. This is academic misconduct.
-
Appropriate use
Research: Using AI to find and analyse information
Pounamu needs to find five academic journal articles for their assignment. They struggle to find relevant results using their keywords, so they ask a GenAI tool to suggest article titles on the topic. Pounamu then goes to OneSearch to verify these articles exist, checks they’re actually relevant to the research question, and accesses them through the library to read and analyse them properly.
Why this works
Pounamu uses AI to overcome a search challenge but verifies everything and engages critically with the actual sources. They do their own reading and analysis.
Inappropriate use
Jamal needs five academic sources but has only found three. He asks a GenAI tool to provide three quotes from academic journals with citations. He adds the quotes and references to his assignment without reading the articles or checking if they’re real.
Why this doesn’t work
GenAI often “hallucinates” fake sources that sound plausible but don’t exist. Jamal hasn’t verified anything and may be citing non-existent articles. He also hasn’t engaged with the actual research.
-
Appropriate use
Creation: Using AI to develop new work
Alex needs to do a systematic review on nutrition and exercise for pregnant people. Because this requires reading a large volume of literature, Alex uses an AI research tool like Elicit to find relevant sources and generate preliminary summaries. Alex uses these summaries to decide which sources to prioritise for full reading, then conducts thorough analysis of the selected literature and writes the systematic review in their own words, citing all sources properly.
Why this works
Alex uses AI to manage the volume of initial source screening - a legitimate efficiency tool for systematic reviews. But all analysis, synthesis, and writing is Alex’s own work.
Inappropriate use
Riria has to do an annotated bibliography with summaries of each article. She copies full articles, pastes them into ChatGPT, and asks it to summarise each text. She uses these summaries directly in her bibliography without reading the articles.
Why this doesn’t work
Riria has uploaded copyrighted material to train AI without permission. She hasn’t engaged with the research and can’t demonstrate understanding. The summaries aren’t her own analytical work.
Tool-specific guidance
Microsoft Copilot (OP-Approved)
Microsoft Copilot is our only OP-approved and supported AI tool because it upholds the privacy and security of our kaimahi and ākonga.
Use Copilot when:
-
You’re working with organisational or institutional information
-
You need AI assistance with OP-related work
-
You want the security of knowing your data won’t be used for training or sold to third parties
AI Tools for checking and improving writing
Some AI tools can help with spelling and grammar, but others pose risks to academic integrity and privacy.
AI Tools
- Microsoft Word - Use the built-in spelling and grammar checks in Word. Avoid Add-in tools, as these often go beyond basic checking and may be considered plagiarism.
- Grammarly (with restrictions) - Grammarly is approved for spelling and grammar checking only. See detailed guidance below.
Avoiding using ChatGPT, Google Gemini, or similar tools to check or improve your writing quality because:
• Privacy and security risks
Anything you input may be used for training data or sold to third parties. Your personal information and work could become searchable by others or used in outputs to other users.
• Turnitin AI detection
Text processed through these tools may receive high AI likelihood percentages in Turnitin reports.
• Paraphrasing = plagiarism
Your work must be in your own words and your own voice. Anything beyond spelling and grammar checks may be considered plagiarism.
Using Grammarly appropriately
Grammarly is approved when used correctly. It uses AI to detect areas for improvement, so it will produce an AI count in Turnitin. Being transparent about how you use tools means that kaiako can take this into consideration.
Follow these steps to avoid academic misconduct issues:
-
Turn off automatic suggestions - Complete your first draft without any Grammarly assistance
-
Save your original draft - Keep this as proof of your own work if needed
-
Upload to Grammarly - Use only for spelling and grammatical checks
-
Save separately - Keep the edited version separate from your original
Grammarly features to avoid
These features would produce writing that is not your own:
| ✗ Autocompleting sentences |
| ✗ Tone changing tools (e.g., changing to “academic” or “formal” language) |
| ✗ Any paraphrasing tools, including “English fluency” features |
| ✗ First draft generation |
| ✗ Grammarly generative AI tool (you can use this to evaluate your writing or brainstorm, but not to create assessment content) |
Paraphrasing tools (Not Approved)
Quillbot and similar paraphrasing tools are not approved. Using paraphrasing tools is inappropriate because:
- Your assessment must be your own ideas in your own words
- You must demonstrate you understand the concepts you’re writing about
- Paraphrasing tools don’t show your teacher that you’ve understood the source material
Reference Managers (Approved)
Reference managers like Zotero, Mendeley, and Endnote are approved tools. They will produce an AI count in Turnitin, so make sure you add them to any AI declaration of use statement you’re required to provide.
AI for research and internet searches
Unfortunately, popular free generative AI tools like ChatGPT and Google Gemini are not reliable search engines. They work by making predictions based on data they have been trained on, rather than retrieving live information. Do not use them for finding information, because you will have to fact-check everything, which is a lot of work.
However, there are reliable AI tools that can help with certain types of research projects, including literature and systematic reviews.
-
For internet searching: use Microsoft Copilot or Perplexity. Always click on citations to verify information from the original source.
-
For academic research: you could try specialised AI research tools like Elicit or Consensus can help with literature reviews and systematic reviews. Verify sources through secondary sources and read the full articles yourself.
Risks to be aware of

Academic misconduct
If you use AI inappropriately in your assignment, you may be found guilty of academic misconduct. There are serious consequences for ākonga who are academically dishonest.
Unreliable information and “hallucinations”
Many GenAI tools are trained on unverified data that may contain:
-
Inaccurate information
-
Misinformation or disinformation
-
Bias
-
Outdated content
Large language models work like predictive text - they predict what should come next based on patterns, not facts. This means they often create information (called “hallucinations”), including fake sources that sound credible but don’t exist, incorrect statistics or dates and made-up quotes and references.
Always verify AI-generated information with reliable sources.
Copyright and plagiarism
-
Some AI tools are trained on copyrighted or licensed data
-
AI cannot produce guaranteed original work
-
Content generated may inadvertently copy existing work
-
Using AI to paraphrase without understanding is still plagiarism
Data privacy
Public GenAI tools may:
-
Collect and store your input data
-
Use your prompts to train algorithms
-
Sell data to third parties
-
Make your information searchable by others
Never input personal information (yours or others’), confidential or sensitive data, work that belongs to someone else or information covered by privacy regulations.
Privacy-focused alternative
DuckDuckGo AI chat, called Duck.ai, anonymises your chats and doesn’t use data for training.
Declaring your AI use
Being transparent about GenAI use reduces the risk of breaching academic integrity policies and demonstrates responsible AI use.
Your kaiako may ask you to complete an AI Declaration of Use form for each assessment. This form helps your teacher understand:
-
Which AI tools you used
-
How you used them
-
What role AI played in your work
Visit the Academic integrity page for more information about using the form.
Attributions
All written content from Academic Integrity: Using AI tools for assignments by Wintec LibGuides. Kind permission to reuse granted from Wintec.
Hero image: An artist’s illustration of artificial intelligence (AI) by Domhnall Malone, part of the Google DeepMind group. Licensed under Pexels.com licence.
Code projected over woman by ThisisEngineering. Licensed under Pexels.com licence.
Robot pointing on a wall projection by Tara Winstead. Licensed under Pexels.com licence.

